34 KiB
(certificates_chapter)=
Certificates / Keys
## What is in a certificate (Structure)
### Subkeys
### User IDs / attributes
- Primary UserID and its implications
### Third party signatures
- Metadata Leak of Social Graph
- How to generate "minimized" certificate?
### Bindings
### Signature Subpackets
- (key-) expiration
- flags
## Certificate Management
### Merging
- How to merge two copies of the same certificate?
- Canonicalization
### Best Practices regarding Key Freshness
- Expiry
- Subkey rotation
One central (and non-trivial) element of OpenPGP are certificates/keys. OpenPGP keys are relatively complex data structures, so it's good to have a clear mental model of them.
Terminology: on the various meanings of "key"
In the OpenPGP space, the term "key" has historically been used for three distinct concepts, at three layers, all related to each other:
- (Bare) "cryptographic keys" (without additional metadata).
Those might be the secret and/or public parameters that form a key, e.g. in case of an RSA secret key the exponent
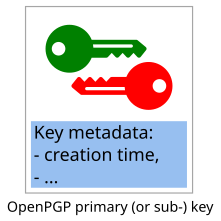
dalong with the prime numberspandq. - OpenPGP component keys: "OpenPGP primary keys" and "OpenPGP subkeys". Those are building blocks of OpenPGP certificates, they consist of a (bare) cryptographic keypair, plus some invariant metadata (e.g. key creation time).
- "OpenPGP key" (or "OpenPGP certificate"): These consist of a number of component keys plus additional elements, such as identity information. (OpenPGP key servers serve this type of object).
In the following section we'll look more closely at these three layers.
"OpenPGP keys/certificates": collections of cryptographic keys, identity information and other metadata
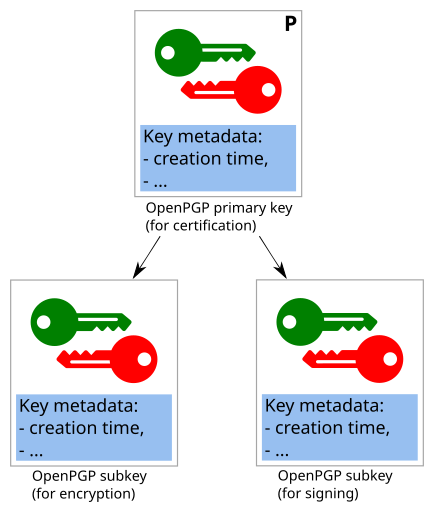
A complete "OpenPGP certificate" or "OpenPGP key" is composed of an arbitrary number of elements.
All elements of an OpenPGP certificate are structured around one central cryptographic key: the primary key. The primary key acts like a personal CA for the key's owner: It can make cryptographic statements about subkeys, identities, expiration times, revocation, ...
OpenPGP keys are often long-lived and may be changed (typically by their owner), over time.
OpenPGP component keys
An OpenPGP component key (either the "primary key", or a "subkey") consists mainly of a cryptographic keypair:
A cryptographic keypair consists of a private and a public part. In this document we'll show the public part of a cryptographic key in green, and the private part in red.
We'll visualize cryptographic keypairs in a more compact form:
(In some contexts, instead of the full cryptographic keypair, only the public part is present. More on that later.)
An OpenPGP component key consists of
- a cryptographic keypair, and
- additional metadata (including a creation timestamp).
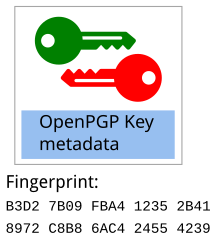
For each OpenPGP component key, an OpenPGP fingerprint can be derived from the combination of key material and metadata:
The fingerprint of our example component OpenPGP key is
B3D2 7B09 FBA4 1235 2B41 8972 C8B8 6AC4 2455 4239 1.
The fingerprint of the primary key has a central role. It is used as the unique identifier for the full OpenPGP certificate.
Components of an OpenPGP key/certificate
In addition to the primary key, OpenPGP keys/certificates can contain a number of other components:
Subkeys
Modern OpenPGP keys/certificates contain "subkeys" in addition to the primary key.
A component key consists of a cryptographic keypair, plus some additional metadata.
Each component key (this includes the primary key, and all subkeys) has a marker that specifies which operations the component key can perform.
Excursion, "Key Flags": defining what operations a component key can perform
Each component key has "Key Flags" that specify which types of operation the key can perform.
The commonly used flags are:
- Certification
- Signing
- Encryption
- Authentication
Only the primary key can perform "certification" operations. All other operations can technically be performed by either the primary key or subkeys.
It is considered good practice to have separate component keys for each type of operation (specifically: to allow only Certification operations for the primary key, and to have separate Signing, Encryption and Authentication subkeys).
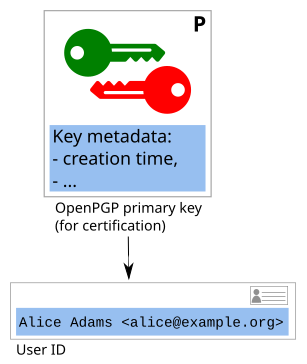
User IDs
An OpenPGP certificate can contain any number of User IDs. Each user ID associates the certificate with an identity.
Typically, these identities are composed of a name and an email address.
User attributes
User attributes are similar to User IDs, but less commonly used.
Linking the components of an OpenPGP certificate together
Technically, an OpenPGP certificate consists of a sequence of OpenPGP packets. These packets are just stringed together, one after the other. When you have a file that contains a copy of someone's certificate, it's easy to remove some of these packets, or add new ones.
However, as the owner of a certificate, I don't want a third party to add additional subkeys (or identity claims) to my certificate. I don't want third parties to pretend that those components were put there by me.
To prevent such malicious addition of components, OpenPGP uses cryptographic signatures. These signatures show the cryptographic identity that has linked a component to an OpenPGP certificate (in many cases, the linking is done by the primary key of the certificate in question).
So while anyone can still unilaterally put subkeys and identity claims into a file with my OpenPGP certificate, OpenPGP implementations that read the file are expected to discard components that aren't cryptographically linked to my certificate.
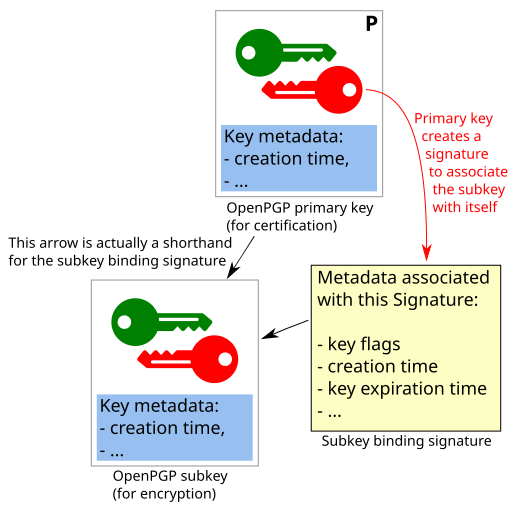
"Binding" subkeys to an OpenPGP certificate
Linking a subkey to an OpenPGP certificate is done with a "Subkey Binding Signature". Such a signature signals that the "primary key wants to be associated with the subkey".
The subkey binding signature also adds metadata.
Binding signing subkeys
When binding a signing subkey to a primary key, it is not sufficient that the "primary key wants to be associated with the subkey". In addition, the subkey must signal that it wants to be associated with that primary key.
Otherwise, Alice could "adopt" Bob's signing subkey and convincingly claim that she made signatures that were in fact issued by Bob.
This additional "Primary Key Binding Signature" is informally called a "back signature" (because the subkey uses the signature to point "back" to the primary key).
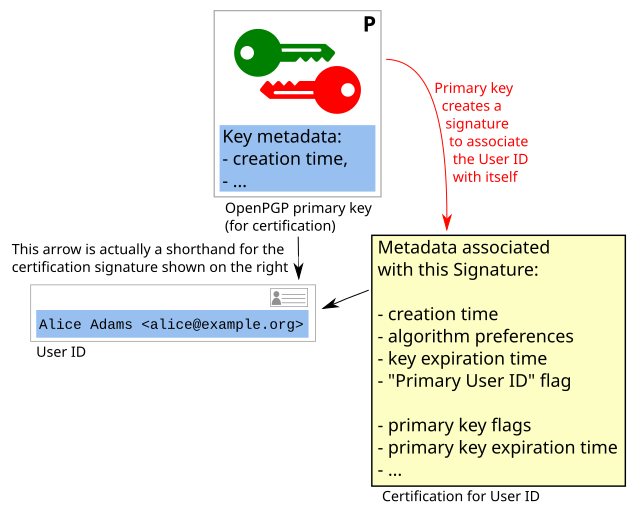
Certifying identity claims
OpenPGP certificate often contain identity markers. Typically in the form of "User ID"s (however, User Attributes are analogous for the purpose of this section).
For example, above, we saw the User ID "Alice Adams alice@example.org"
associated with Alice's key B3D2 7B09 FBA4 1235 2B41 8972 C8B8 6AC4 2455 4239.
Alice can link a User ID to her OpenPGP certificate with a cryptographic
signature. To link a User ID, a signature of the type PositiveCertification
is created. The signature is issued using the primary (secret) key.
Evolution of a certificate over time
Minimized versions, merging, effective "append only" semantics, ...
Third party (identity) certifications
Revocations
Looking at the internal details
To use OpenPGP, we need "(OpenPGP) keys".
There is an ongoing effort to establish new terminology around "keys". In particular to use the term "certificate" instead of "(OpenPGP) public key".
Note: there is also the related, but distinct, concept of cryptographic "keys". OpenPGP certificates/keys contain one or more cryptographic key(s), among many other components.
An OpenPGP certificate/key consists of a number of elements, many of them optional. OpenPGP certificates/keys always make use of Public-key cryptography (asymmetric cryptography).
As a consequence, some elements of OpenPGP certificates/keys represent "private" (sometimes referred to as "secret") key material, while other elements represent "public" key material. Yet other elements contain metadata, and finally there are elements that serve as glue ("binding") between the various other elements of a certificate.
To hand out copies of one's OpenPGP key to third parties, implementations can generate a "certificate" / "public key" representation (Transferable Public Keys in the RFC), which consists of all the elements of the certificate, except for the private key material (and the optional S2K configuration).
The counterpart is called Transferable Secret Keys in the RFC. That is, an OpenPGP key that includes private key material.
A minimal OpenPGP key
A minimal key can be made with Sequoia-PGP like this:
let (cert, _) = CertBuilder::new().generate()?;
Seen as a private OpenPGP key
Viewed as a private key (in ASCII-armored representation), such a minimal key looks like this:
-----BEGIN PGP PRIVATE KEY BLOCK-----
Comment: 6D10 0EB0 444D 1648 DAD9 A0EE DE83 CCF4 A204 F957
xVgEX7Kj9hYJKwYBBAHaRw8BAQdAztZjmUk3IUgnKwR9rfukVUt7UaVsvk+AoBtO
ZNbVqDcAAP4nrycHrmWHT8g454H/tr/19rT0nuPkYxMCUH9z5Atx/xLYwoMEHxYK
ADUFgl+yo/YDCwkHCRDeg8z0ogT5VwMVCggCmwECHgEWIQRtEA6wRE0WSNrZoO7e
g8z0ogT5VwAAbFgBAO1OYraoaDmFMZ7JWbLoTKW7xpDUNKB+kh+bdC6HjYpcAP9q
HhhgNE7noeQEsJmR0yW7tTYT8RyrJF6o2xZENlXdCw==
=/8Os
-----END PGP PRIVATE KEY BLOCK-----
Looking into the internals of this key with sq packet dump --hex,
or https://dump.sequoia-pgp.org/, we see that it is made up of a sequence
of "Packets":
Secret-Key Packet, new CTB, 2 header bytes + 88 bytes
Version: 4
Creation time: 2020-11-16 16:08:22 UTC
Pk algo: EdDSA Edwards-curve Digital Signature Algorithm
Pk size: 256 bits
Fingerprint: 6D10 0EB0 444D 1648 DAD9 A0EE DE83 CCF4 A204 F957
KeyID: DE83 CCF4 A204 F957
Secret Key:
Unencrypted
00000000 c5 CTB
00000001 58 length
00000002 04 version
00000003 5f b2 a3 f6 creation_time
00000007 16 pk_algo
00000008 09 curve_len
00000009 2b 06 01 04 01 da 47 curve
00000010 0f 01
00000012 01 07 eddsa_public_len
00000014 40 ce d6 63 99 49 37 21 48 27 2b 04 eddsa_public
00000020 7d ad fb a4 55 4b 7b 51 a5 6c be 4f 80 a0 1b 4e
00000030 64 d6 d5 a8 37
00000035 00 s2k_usage
00000036 00 fe eddsa_secret_len
00000038 27 af 27 07 ae 65 87 4f eddsa_secret
00000040 c8 38 e7 81 ff b6 bf f5 f6 b4 f4 9e e3 e4 63 13
00000050 02 50 7f 73 e4 0b 71 ff
00000058 12 d8 checksum
Signature Packet, new CTB, 2 header bytes + 131 bytes
Version: 4
Type: DirectKey
Pk algo: EdDSA Edwards-curve Digital Signature Algorithm
Hash algo: SHA512
Hashed area:
Signature creation time: 2020-11-16 16:08:22 UTC (critical)
Symmetric algo preferences: AES256, AES128
Issuer: DE83 CCF4 A204 F957
Hash preferences: SHA512, SHA256
Key flags: C (critical)
Features: MDC
Issuer Fingerprint: 6D10 0EB0 444D 1648 DAD9 A0EE DE83 CCF4 A204 F957
Digest prefix: 6C58
Level: 0 (signature over data)
00000000 c2 CTB
00000001 83 length
00000002 04 version
00000003 1f type
00000004 16 pk_algo
00000005 0a hash_algo
00000006 00 35 hashed_area_len
00000008 05 subpacket length
00000009 82 subpacket tag
0000000a 5f b2 a3 f6 sig creation time
0000000e 03 subpacket length
0000000f 0b subpacket tag
00000010 09 07 pref sym algos
00000012 09 subpacket length
00000013 10 subpacket tag
00000014 de 83 cc f4 a2 04 f9 57 issuer
0000001c 03 subpacket length
0000001d 15 subpacket tag
0000001e 0a 08 pref hash algos
00000020 02 subpacket length
00000021 9b subpacket tag
00000022 01 key flags
00000023 02 subpacket length
00000024 1e subpacket tag
00000025 01 features
00000026 16 subpacket length
00000027 21 subpacket tag
00000028 04 version
00000029 6d 10 0e b0 44 4d 16 issuer fp
00000030 48 da d9 a0 ee de 83 cc f4 a2 04 f9 57
0000003d 00 00 unhashed_area_len
0000003f 6c digest_prefix1
00000040 58 digest_prefix2
00000041 01 00 eddsa_sig_r_len
00000043 ed 4e 62 b6 a8 68 39 85 31 9e c9 59 b2 eddsa_sig_r
00000050 e8 4c a5 bb c6 90 d4 34 a0 7e 92 1f 9b 74 2e 87
00000060 8d 8a 5c
00000063 00 ff eddsa_sig_s_len
00000065 6a 1e 18 60 34 4e e7 a1 e4 04 b0 eddsa_sig_s
00000070 99 91 d3 25 bb b5 36 13 f1 1c ab 24 5e a8 db 16
00000080 44 36 55 dd 0b
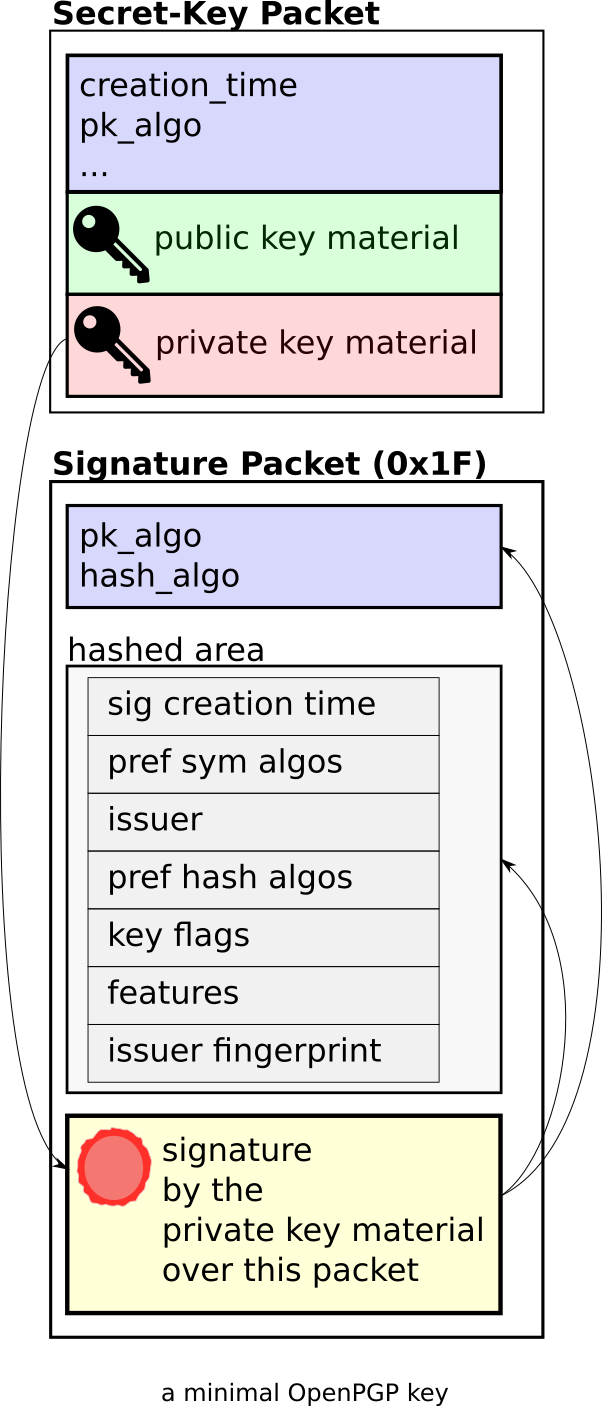
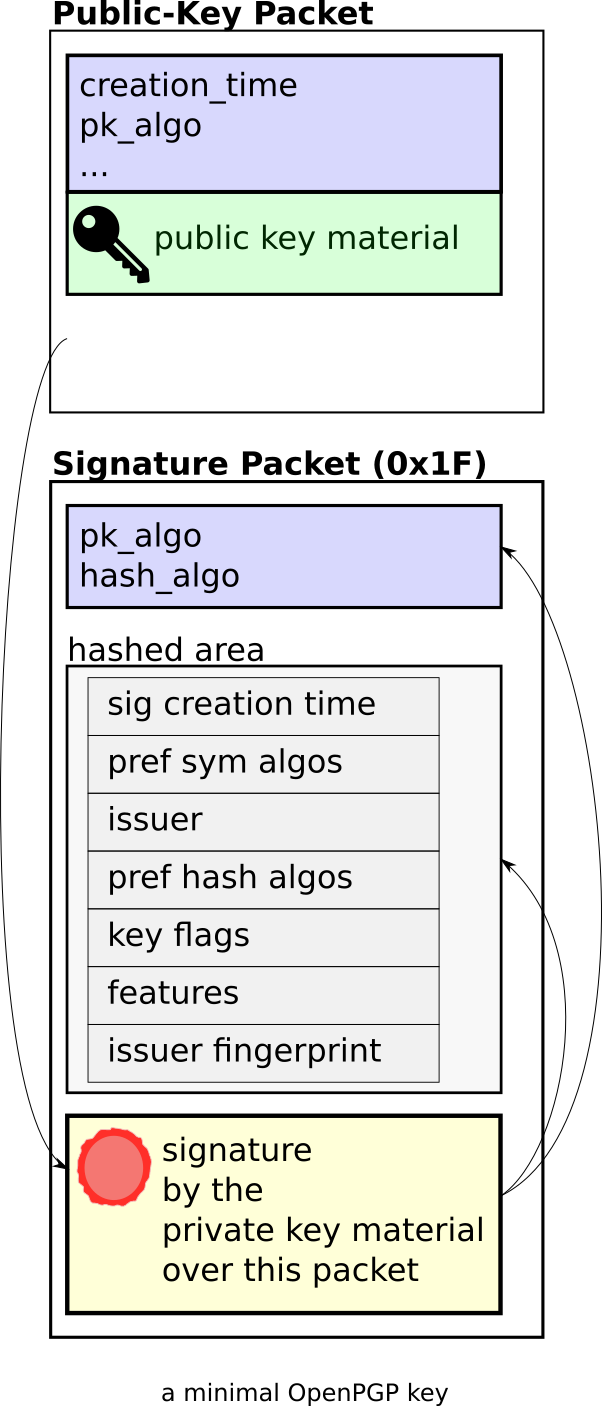
We see that the key consists of two packets:
- First a "Secret-Key Packet", which contains the actual cryptographic key data. Note: the "Secret-Key" Packet contains both the private and the public part of the key. We also see in the output that this packet is "Unencrypted" (i.e. not password-protected).
- Second a "Signature Packet" of type 0x1F, "Signature directly on a key". This packet "binds the information in the Signature subpackets to the key". Each entry under "Signature Packet -> Hashed area" is one Signature subpacket, including for example information about algorithm preferences ("Symmetric algo preferences" and "Hash preferences").
Seen as a public certificate
Let's compare this with the same certificate seen as an armored "public" certificate (that is, a variant of the key above, but without the private key material. An OpenPGP user might give such a certificate to a communication partner, so that the remote party could send encrypted messages to the user):
-----BEGIN PGP PUBLIC KEY BLOCK-----
Comment: 6D10 0EB0 444D 1648 DAD9 A0EE DE83 CCF4 A204 F957
xjMEX7Kj9hYJKwYBBAHaRw8BAQdAztZjmUk3IUgnKwR9rfukVUt7UaVsvk+AoBtO
ZNbVqDfCgwQfFgoANQWCX7Kj9gMLCQcJEN6DzPSiBPlXAxUKCAKbAQIeARYhBG0Q
DrBETRZI2tmg7t6DzPSiBPlXAABsWAEA7U5itqhoOYUxnslZsuhMpbvGkNQ0oH6S
H5t0LoeNilwA/2oeGGA0Tueh5ASwmZHTJbu1NhPxHKskXqjbFkQ2Vd0L
=ZN14
-----END PGP PUBLIC KEY BLOCK-----
Public-Key Packet, new CTB, 2 header bytes + 51 bytes
Version: 4
Creation time: 2020-11-16 16:08:22 UTC
Pk algo: EdDSA Edwards-curve Digital Signature Algorithm
Pk size: 256 bits
Fingerprint: 6D10 0EB0 444D 1648 DAD9 A0EE DE83 CCF4 A204 F957
KeyID: DE83 CCF4 A204 F957
00000000 c6 CTB
00000001 33 length
00000002 04 version
00000003 5f b2 a3 f6 creation_time
00000007 16 pk_algo
00000008 09 curve_len
00000009 2b 06 01 04 01 da 47 curve
00000010 0f 01
00000012 01 07 eddsa_public_len
00000014 40 ce d6 63 99 49 37 21 48 27 2b 04 eddsa_public
00000020 7d ad fb a4 55 4b 7b 51 a5 6c be 4f 80 a0 1b 4e
00000030 64 d6 d5 a8 37
00000035 s2k_usage
Signature Packet, new CTB, 2 header bytes + 131 bytes
Version: 4
Type: DirectKey
Pk algo: EdDSA Edwards-curve Digital Signature Algorithm
Hash algo: SHA512
Hashed area:
Signature creation time: 2020-11-16 16:08:22 UTC (critical)
Symmetric algo preferences: AES256, AES128
Issuer: DE83 CCF4 A204 F957
Hash preferences: SHA512, SHA256
Key flags: C (critical)
Features: MDC
Issuer Fingerprint: 6D10 0EB0 444D 1648 DAD9 A0EE DE83 CCF4 A204 F957
Digest prefix: 6C58
Level: 0 (signature over data)
00000000 c2 CTB
00000001 83 length
00000002 04 version
00000003 1f type
00000004 16 pk_algo
00000005 0a hash_algo
00000006 00 35 hashed_area_len
00000008 05 subpacket length
00000009 82 subpacket tag
0000000a 5f b2 a3 f6 sig creation time
0000000e 03 subpacket length
0000000f 0b subpacket tag
00000010 09 07 pref sym algos
00000012 09 subpacket length
00000013 10 subpacket tag
00000014 de 83 cc f4 a2 04 f9 57 issuer
0000001c 03 subpacket length
0000001d 15 subpacket tag
0000001e 0a 08 pref hash algos
00000020 02 subpacket length
00000021 9b subpacket tag
00000022 01 key flags
00000023 02 subpacket length
00000024 1e subpacket tag
00000025 01 features
00000026 16 subpacket length
00000027 21 subpacket tag
00000028 04 version
00000029 6d 10 0e b0 44 4d 16 issuer fp
00000030 48 da d9 a0 ee de 83 cc f4 a2 04 f9 57
0000003d 00 00 unhashed_area_len
0000003f 6c digest_prefix1
00000040 58 digest_prefix2
00000041 01 00 eddsa_sig_r_len
00000043 ed 4e 62 b6 a8 68 39 85 31 9e c9 59 b2 eddsa_sig_r
00000050 e8 4c a5 bb c6 90 d4 34 a0 7e 92 1f 9b 74 2e 87
00000060 8d 8a 5c
00000063 00 ff eddsa_sig_s_len
00000065 6a 1e 18 60 34 4e e7 a1 e4 04 b0 eddsa_sig_s
00000070 99 91 d3 25 bb b5 36 13 f1 1c ab 24 5e a8 db 16
00000080 44 36 55 dd 0b
Note that the two OpenPGP artifacts (public certificate and private key) are almost identical.
The public certificate uses the packet type "Public-Key Packet" instead of "Secret-Key Packet". The two packet types are very similar. The "Public-Key Packet" leaves out two types of data
- the private key material (visualized in red), and
- s2k configuration data, if any (this example doesn't have any). s2k is used when the secret key material is password-protected.
In following examples we will look at OpenPGP private keys only. The corresponding public certificates are easy to imagine (just leave out the private key material).
User IDs
User IDs are a mechanism for attaching identities to an OpenPGP certificate. Typically, a User ID will contain a name and an email address.
To look into these, we'll make a certificate that has one User ID. User IDs are "intended to represent the name and email address of the key holder". A certificate can have multiple User IDs associated with it.
let (cert, _) = CertBuilder::new()
.add_userid("Alice Adams <alice@example.org>")
.generate()?;
Let's look into the details of this key:
-----BEGIN PGP PRIVATE KEY BLOCK-----
Comment: A3F3 1A57 E400 A77C 2239 24C0 783B 4E35 B4E5 F1BA
Comment: Alice Adams <alice@example.org>
xVgEX7LO1RYJKwYBBAHaRw8BAQdAiDI09+r0a4BVBUZCIqdSF9yuC706fRNC6tvZ
zReMlI4AAP0VhUQxbMmXjJgXfiH2p0Zo/1G9WgC2h5HwfluLGONYJQ/+woMEHxYK
ADUFgl+yztUDCwkHCRB4O041tOXxugMVCggCmwECHgEWIQSj8xpX5ACnfCI5JMB4
O041tOXxugAAfXwBAPkjwkSO5aI3lQUNi/h4OiwPUF/u6AO9rHsg45WURZOwAQDy
8TQHQyFR52QjldVYbevffMaWfBiB4LfmrMeNvoHNC80fQWxpY2UgQWRhbXMgPGFs
aWNlQGV4YW1wbGUub3JnPsKGBBMWCgA4BYJfss7VAwsJBwkQeDtONbTl8boDFQoI
ApkBApsBAh4BFiEEo/MaV+QAp3wiOSTAeDtONbTl8boAALLzAP4oGNBkrnpv7TBi
cucUcQZbAURxRDZLioWmwu/VVqWRQwEAk/3oG5sP327lu73CE7LUjBt5ChtAlDlP
szWqa9TiCw4=
=tnJI
-----END PGP PRIVATE KEY BLOCK-----
Secret-Key Packet, new CTB, 2 header bytes + 88 bytes
Version: 4
Creation time: 2020-11-16 19:11:17 UTC
Pk algo: EdDSA Edwards-curve Digital Signature Algorithm
Pk size: 256 bits
Fingerprint: A3F3 1A57 E400 A77C 2239 24C0 783B 4E35 B4E5 F1BA
KeyID: 783B 4E35 B4E5 F1BA
Secret Key:
Unencrypted
00000000 c5 CTB
00000001 58 length
00000002 04 version
00000003 5f b2 ce d5 creation_time
00000007 16 pk_algo
00000008 09 curve_len
00000009 2b 06 01 04 01 da 47 curve
00000010 0f 01
00000012 01 07 eddsa_public_len
00000014 40 88 32 34 f7 ea f4 6b 80 55 05 46 eddsa_public
00000020 42 22 a7 52 17 dc ae 0b bd 3a 7d 13 42 ea db d9
00000030 cd 17 8c 94 8e
00000035 00 s2k_usage
00000036 00 fd eddsa_secret_len
00000038 15 85 44 31 6c c9 97 8c eddsa_secret
00000040 98 17 7e 21 f6 a7 46 68 ff 51 bd 5a 00 b6 87 91
00000050 f0 7e 5b 8b 18 e3 58 25
00000058 0f fe checksum
Signature Packet, new CTB, 2 header bytes + 131 bytes
Version: 4
Type: DirectKey
Pk algo: EdDSA Edwards-curve Digital Signature Algorithm
Hash algo: SHA512
Hashed area:
Signature creation time: 2020-11-16 19:11:17 UTC (critical)
Symmetric algo preferences: AES256, AES128
Issuer: 783B 4E35 B4E5 F1BA
Hash preferences: SHA512, SHA256
Key flags: C (critical)
Features: MDC
Issuer Fingerprint: A3F3 1A57 E400 A77C 2239 24C0 783B 4E35 B4E5 F1BA
Digest prefix: 7D7C
Level: 0 (signature over data)
00000000 c2 CTB
00000001 83 length
00000002 04 version
00000003 1f type
00000004 16 pk_algo
00000005 0a hash_algo
00000006 00 35 hashed_area_len
00000008 05 subpacket length
00000009 82 subpacket tag
0000000a 5f b2 ce d5 sig creation time
0000000e 03 subpacket length
0000000f 0b subpacket tag
00000010 09 07 pref sym algos
00000012 09 subpacket length
00000013 10 subpacket tag
00000014 78 3b 4e 35 b4 e5 f1 ba issuer
0000001c 03 subpacket length
0000001d 15 subpacket tag
0000001e 0a 08 pref hash algos
00000020 02 subpacket length
00000021 9b subpacket tag
00000022 01 key flags
00000023 02 subpacket length
00000024 1e subpacket tag
00000025 01 features
00000026 16 subpacket length
00000027 21 subpacket tag
00000028 04 version
00000029 a3 f3 1a 57 e4 00 a7 issuer fp
00000030 7c 22 39 24 c0 78 3b 4e 35 b4 e5 f1 ba
0000003d 00 00 unhashed_area_len
0000003f 7d digest_prefix1
00000040 7c digest_prefix2
00000041 01 00 eddsa_sig_r_len
00000043 f9 23 c2 44 8e e5 a2 37 95 05 0d 8b f8 eddsa_sig_r
00000050 78 3a 2c 0f 50 5f ee e8 03 bd ac 7b 20 e3 95 94
00000060 45 93 b0
00000063 01 00 eddsa_sig_s_len
00000065 f2 f1 34 07 43 21 51 e7 64 23 95 eddsa_sig_s
00000070 d5 58 6d eb df 7c c6 96 7c 18 81 e0 b7 e6 ac c7
00000080 8d be 81 cd 0b
User ID Packet, new CTB, 2 header bytes + 31 bytes
Value: Alice Adams <alice@example.org>
00000000 cd CTB
00000001 1f length
00000002 41 6c 69 63 65 20 41 64 61 6d 73 20 3c 61 value
00000010 6c 69 63 65 40 65 78 61 6d 70 6c 65 2e 6f 72 67
00000020 3e
Signature Packet, new CTB, 2 header bytes + 134 bytes
Version: 4
Type: PositiveCertification
Pk algo: EdDSA Edwards-curve Digital Signature Algorithm
Hash algo: SHA512
Hashed area:
Signature creation time: 2020-11-16 19:11:17 UTC (critical)
Symmetric algo preferences: AES256, AES128
Issuer: 783B 4E35 B4E5 F1BA
Hash preferences: SHA512, SHA256
Primary User ID: true (critical)
Key flags: C (critical)
Features: MDC
Issuer Fingerprint: A3F3 1A57 E400 A77C 2239 24C0 783B 4E35 B4E5 F1BA
Digest prefix: B2F3
Level: 0 (signature over data)
00000000 c2 CTB
00000001 86 length
00000002 04 version
00000003 13 type
00000004 16 pk_algo
00000005 0a hash_algo
00000006 00 38 hashed_area_len
00000008 05 subpacket length
00000009 82 subpacket tag
0000000a 5f b2 ce d5 sig creation time
0000000e 03 subpacket length
0000000f 0b subpacket tag
00000010 09 07 pref sym algos
00000012 09 subpacket length
00000013 10 subpacket tag
00000014 78 3b 4e 35 b4 e5 f1 ba issuer
0000001c 03 subpacket length
0000001d 15 subpacket tag
0000001e 0a 08 pref hash algos
00000020 02 subpacket length
00000021 99 subpacket tag
00000022 01 primary user id
00000023 02 subpacket length
00000024 9b subpacket tag
00000025 01 key flags
00000026 02 subpacket length
00000027 1e subpacket tag
00000028 01 features
00000029 16 subpacket length
0000002a 21 subpacket tag
0000002b 04 version
0000002c a3 f3 1a 57 issuer fp
00000030 e4 00 a7 7c 22 39 24 c0 78 3b 4e 35 b4 e5 f1 ba
00000040 00 00 unhashed_area_len
00000042 b2 digest_prefix1
00000043 f3 digest_prefix2
00000044 00 fe eddsa_sig_r_len
00000046 28 18 d0 64 ae 7a 6f ed 30 62 eddsa_sig_r
00000050 72 e7 14 71 06 5b 01 44 71 44 36 4b 8a 85 a6 c2
00000060 ef d5 56 a5 91 43
00000066 01 00 eddsa_sig_s_len
00000068 93 fd e8 1b 9b 0f df 6e eddsa_sig_s
00000070 e5 bb bd c2 13 b2 d4 8c 1b 79 0a 1b 40 94 39 4f
00000080 b3 35 aa 6b d4 e2 0b 0e
Instead of two sections, as before, we see four sections in this certificate:
- First a "Secret-Key Packet",
- then a "Signature Packet" (these two packets are the same as above).
- Third, a "User ID Packet", which contains the name and email address we used
- Finally a "Signature Packet" of type 0x13, "Positive certification of a User ID and Public-Key packet". This is a cryptographic artifact that "binds the User ID packet and the Key packet together", i.e. it certifies that the owner of the key wants this User ID associated with their key. (Only the person who controls the private part of this key can create this signature packet. The signature serves as proof that the owner of the key has added this User ID to the certificate)
Subkeys
From here on, we'll look at the dumps in shorter format (you can see more detail by copying the certificates into the web-dumper at https://dump.sequoia-pgp.org/ and checking the "HexDump" checkbox).
Certifications (Signatures)
Revocations
-
Sometimes, a shortened (64 bit) version of the fingerprint is used instead of the full fingerprint, like this:
C8B8 6AC4 2455 4239(the rightmost 64 bit of the fingerprint). This type of identifier is called a "Key ID".
Historically, 32 bit shorthand identifiers have been used with PGP, like this:2455 4239. You may still see such identifiers in very old documents about PGP, but 32 bit identifiers have been unfit for purpose for a long time.
At some point, 32 bit identifiers were called "short Key ID", while 64 bit identifiers were called "long Key ID". ↩︎